Publications
This section lists the selections of my publications in time order.
You can also find my articles on my Google Scholar profile, and my academic activities on my ORCID.
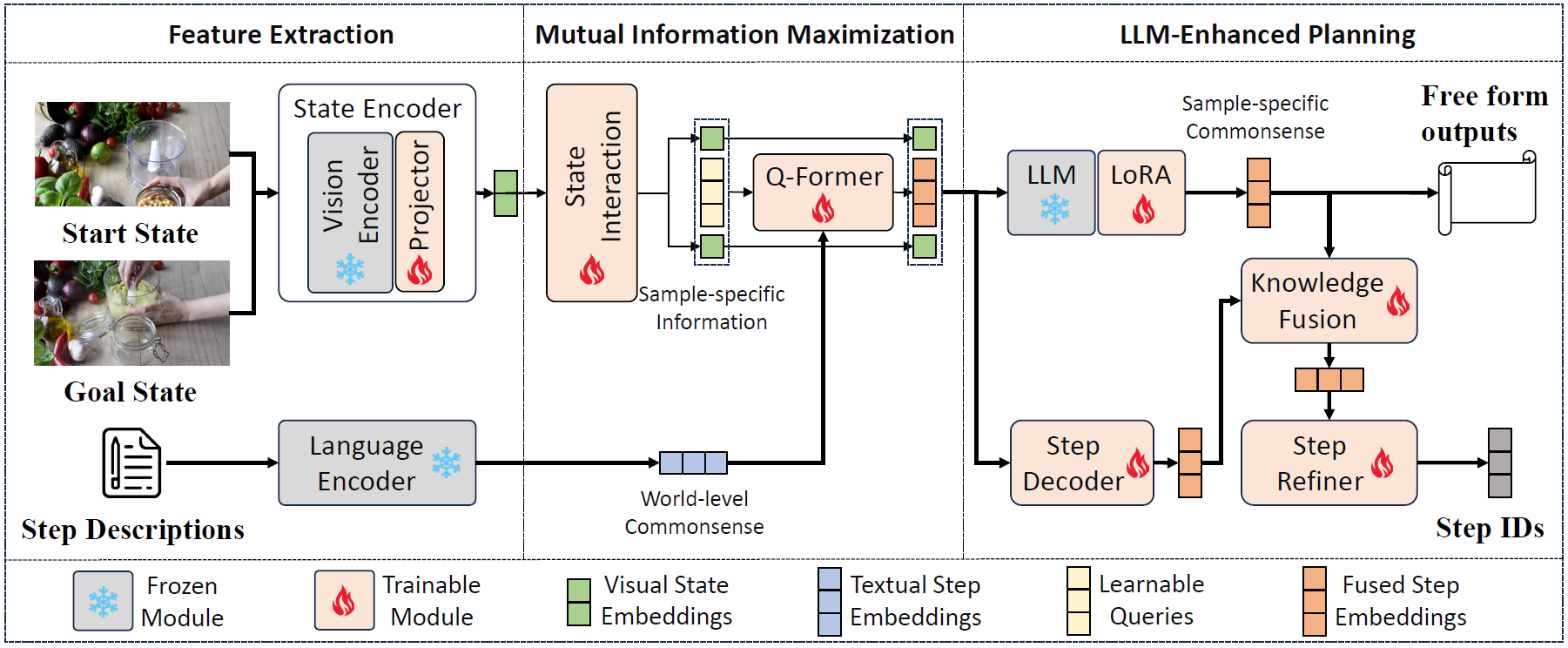
PlanLLM: Video Procedure Planning with Refinable Large Language Models
Dejie Yang, Zijing Zhao and Yang Liu†
Published on The AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2025) (CCF-A)
[pdf] [code] [project page]
Abstract (Click to unfold):
Video procedure planning, ie, planning a sequence of action steps given the video frames of start and goal states, is an essential ability for embodied AI. Recent works utilize Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate enriched action step description texts to guide action step decoding. Although LLMs are introduced these methods decode the action steps into a closed-set of one-hot vectors, limiting the model's capability of generalizing to new steps or tasks. Additionally, fixed action step descriptions based on world-level commonsense may contain noise in specific instances of visual states. In this paper, we propose PlanLLM, a cross-modal joint learning framework with LLMs for video procedure planning. We propose an LLM-Enhanced Planning module which fully uses the generalization ability of LLMs to produce free-form planning output and to enhance action step decoding. We also propose Mutual Information Maximization module to connect world-level commonsense of step descriptions and sample-specific information of visual states, enabling LLMs to employ the reasoning ability to generate step sequences. With the assistance of LLMs, our method can both closed-set and open vocabulary procedure planning tasks. Our PlanLLM achieves superior performance on three benchmarks, demonstrating the effectiveness of our designs.Masked Retraining Teacher-student Framework for Domain Adaptive Object Detection
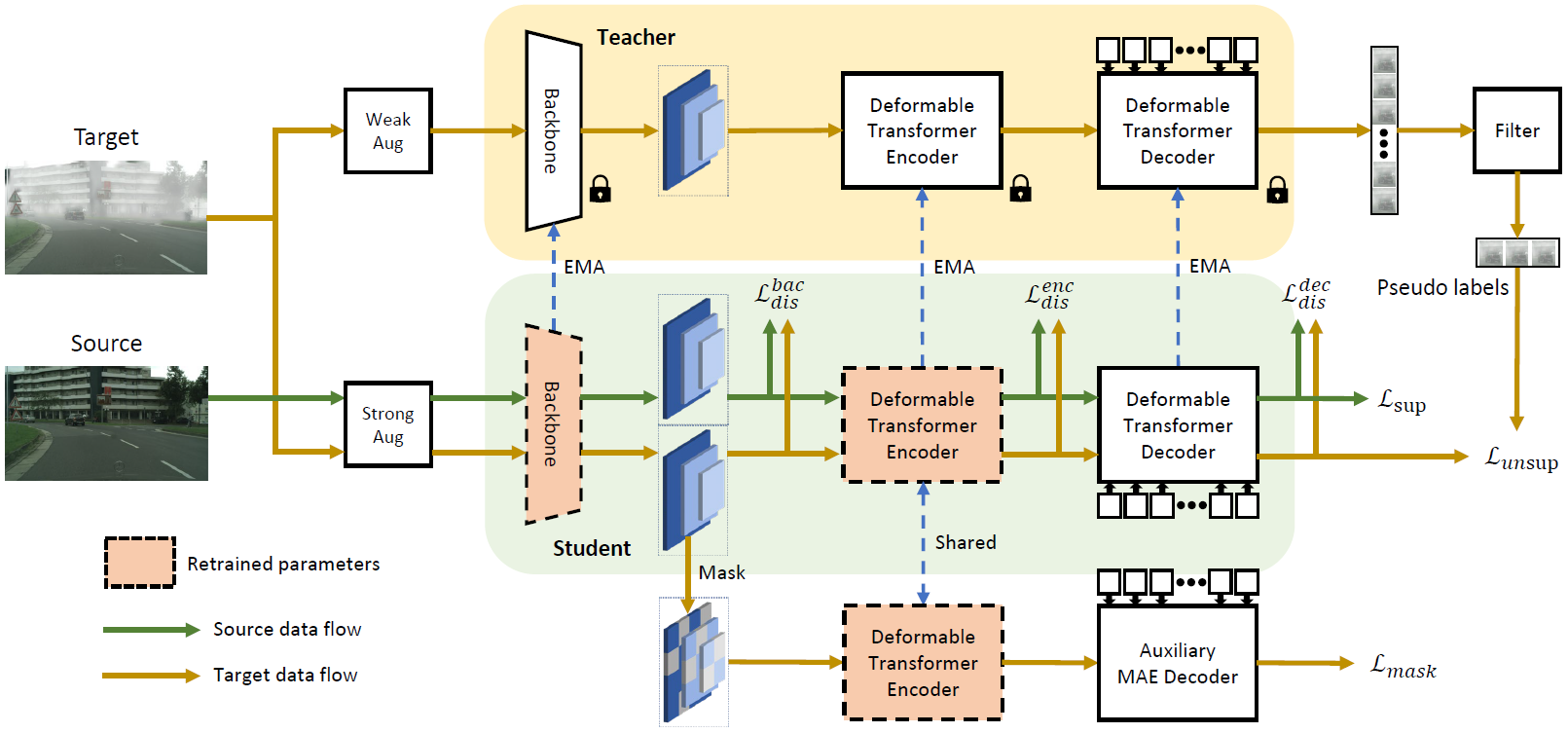
Zijing Zhao, Sitong Wei, Qingchao Chen, Dehui Li, Yifan Yang, Yuxin Peng and Yang Liu†
Published on International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2023) (CCF-A)
[pdf] [supp] [code] [homepage]
Abstract (Click to unfold):
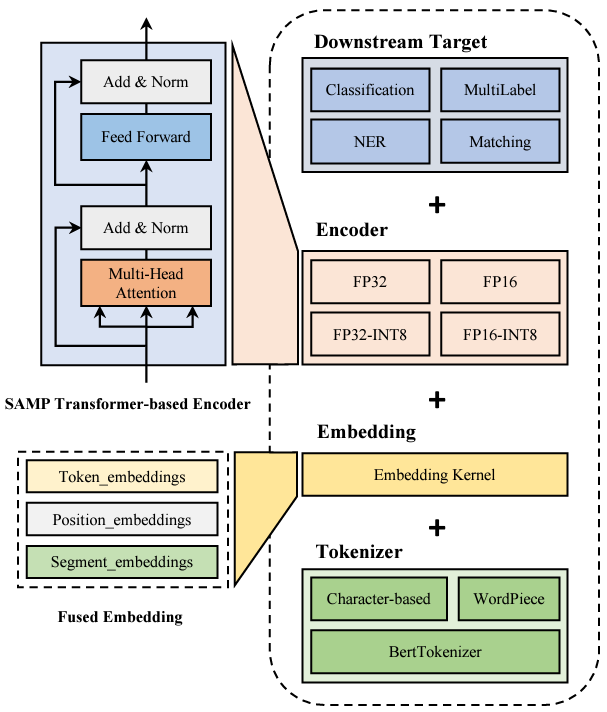
Domain adaptive Object Detection (DAOD) leverages a labeled domain (source) to learn an object detector generalizing to a novel domain without annotation (target). Recent advances use a teacher-student framework, i.e., a student model is supervised by the pseudo labels from a teacher model. Though great success, they suffer from the limited number of pseudo boxes with incorrect predictions caused by the domain shift, misleading the student model to get sub-optimal results. To mitigate this problem, we propose Masked Retraining Teacher-student framework (MRT) which leverages masked autoencoder and selective retraining mechanism on detection transformer. Specifically, we present a customized design of masked autoencoder branch, masking the multi-scale feature maps of target images and reconstructing features by the encoder of the student model and an auxiliary decoder. This helps the student model capture target domain characteristics and become a more data-efficient learner to gain knowledge from the limited number of pseudo boxes. Furthermore, we adopt selective retraining mechanism, periodically re-initializing certain parts of the student parameters with masked autoencoder refined weights to allow the model to jump out of the local optimum biased to the incorrect pseudo labels. Experimental results on three DAOD benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.SAMP: A Model Inference Toolkit of Post-Training Quantization for Text Processing via Self-Adaptive Mixed-Precision
Rong Tian†, Zijing Zhao, Weijie Liu, Haoyan Liu, Weiquan Mao, Zhe Zhao and Kan Zhou
Published on Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: Industry Track (EMNLP 2023) (CCF-B)
[pdf]